Events
The following events can be used as extension points to intervene and manipulate data:
| Event | Description | Available since |
|---|---|---|
preFileProcessing | Execute custom logic before processing the spreadsheet file starts | 1.2.0 |
checkBeforeRead | Check data before it is uploaded to the UI5 | Initial release |
changeBeforeCreate | Change data before it is sent to the backend | Initial release |
requestCompleted | Event when the request is completed | 0.28.0 |
uploadButtonPress | Fired when the Upload button is pressed, possible to prevent data from being sent to the backend | 0.13.0 |
beforeDownloadFileProcessing | Fired before the data is converted to a spreadsheet file | 1.5.0 |
beforeDownloadFileExport | Fired just before the file is downloaded | 1.5.0 |
You can attach async functions to the events by wrapping the function in a Promise. See Attach async functions to events for more information.
Event preFileProcessing¶
When the file is uploaded to the app, the preFileProcessing event is fired. Use this event to execute custom logic before processing the spreadsheet file starts. The file is available in the event and can be manipulated. If you want to prevent the processing of the file, call the preventDefault method of the event. If you want to change the file that will be processed, return the new file.
Example¶
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachPreFileProcessing(function (event) {
// example
let file = event.getParameter('file');
if (file.name.endsWith('.txt')) {
// prevent processing of file
event.preventDefault();
// show custom ui5 error message
new MessageToast.show('File with .txt extension is not allowed');
// change the file that will be processed
// Create a Blob with some text content
const blob = new Blob(['This is some dummy text content'], { type: 'text/plain' });
// Create a File object from the Blob
const file2 = new File([blob], 'TEXT.txt', { type: 'text/plain' });
return file2;
}
});
Event checkBeforeRead¶
When the file is uploaded to the app, the checkBeforeRead event is fired.
Example¶
This sample is from the sample app. It checks whether the price is over 100.
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachCheckBeforeRead(function (event) {
// example
const sheetdata = event.getParameter('sheetData');
let errorArray = [];
for (const [index, row] of sheetData.entries()) {
// Check for invalid price
for (const key in row) {
if (key.endsWith('[price]') && row[key].rawValue > 100) {
const error = {
title: 'Price too high (max 100)',
row: index + 2,
group: true,
rawValue: row[key].rawValue,
ui5type: 'Error'
};
errorArray.push(error);
}
}
}
event.getSource().addArrayToMessages(errorArray);
}, this);
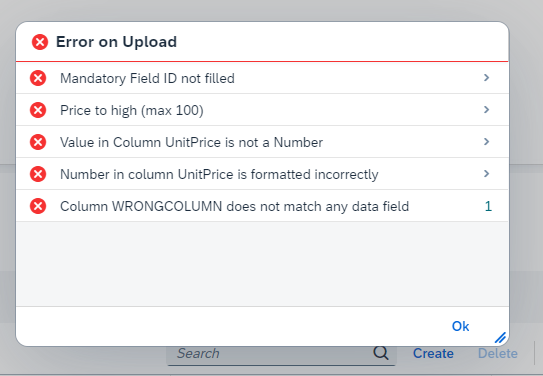
You can add errors to the messages property of the SpreadsheetUpload control. After the event, the upload is canceled and the errors are displayed in the error dialog. Use the addArrayToMessages method to add errors to the messages property. It expects an array of objects with the following properties:
title- the title of the errorrow- the row number of the errorgroup- set totrueorfalseto group the errors by titlerawValue- the raw value of the data from the spreadsheetui5type- the type of the error, can beError,Warning,Success,InformationorNonefrom the `MessageType enum
Errors with the same title will be grouped.
Event changeBeforeCreate¶
When the Upload button is pressed, the changeBeforeCreate event is fired. Use this event to manipulate the data before it is sent to the backend. The event expects a payload object to be returned.
Make sure only one handler is attached to this event. If multiple handlers are attached, only the first payload will be used.
Example¶
This sample is from the sample app. It overwrites the payload.
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachChangeBeforeCreate(function (event) {
let payload = event.getParameter('payload');
// round number from 12,56 to 12,6
if (payload.price) {
payload.price = Number(payload.price.toFixed(1));
}
return payload;
}, this);
Event requestCompleted¶
When the request is completed, the requestCompleted event is fired. Use the success parameter to check if the request was successful.
Example¶
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachRequestCompleted(function (event) {
const success = event.getParameter('success');
if (success) {
console.log('Request Completed');
} else {
console.log('Request Failed');
}
}, this);
Event uploadButtonPress¶
When the Upload button is pressed, the uploadButtonPress event is fired. The event is fired before the changeBeforeCreate event. Prevent the data from being sent to the backend by calling the preventDefault method of the event.
Example 1¶
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachUploadButtonPress(function (event) {
// Prevent data from being sent to the backend
event.preventDefault();
// Get payload
const payload = event.getParameter('payload');
}, this);
Example 2¶
You can also use this event to sent the data to the backend and add possible errors to the component. Use the addArrayToMessages method to add errors. It will display the errors in the error dialog after the execution of the event.
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachUploadButtonPress(async function (event) {
event.preventDefault();
event.getSource().addArrayToMessages([
{
title: 'Error on creating',
group: false,
ui5type: 'Error'
}
]);
// simulate async call
await new Promise(resolve => {
// Wait for 2 seconds
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 2000);
});
// Code here will execute after the 2-second wait
}, this);
Event beforeDownloadFileProcessing¶
Parameters:
data- the data that will be converted to a spreadsheet file, the data is always the$XYZDataproperty of the data object
This event is fired before the data is converted to a spreadsheet file. Use this event to manipulate the data before it is converted.
You can change directly the data parameter of the event as this is a reference to the data.
Example¶
onDownload: async function () {
// init your spreadsheet upload component
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachBeforeDownloadFileProcessing(this.onBeforeDownloadFileProcessing, this);
this.spreadsheetUpload.triggerDownloadSpreadsheet();
},
onBeforeDownloadFileProcessing: function (event) {
const data = event.getParameters().data;
// change buyer of first row of the root entity
data.$XYZData[0].buyer = "Customer 123";
// change quantity of first row of the Items entity
data.Items.$XYZData[0].quantity = 4
}
Event beforeDownloadFileExport¶
Parameters:
workbook- the SheetJS workbook objectfilename- the filename of the file that will be downloaded
This event is fired just before the file is downloaded. Use this event to manipulate the filename or other parameters before the file is downloaded.
Example¶
onDownload: async function () {
// init your spreadsheet upload component
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachBeforeDownloadFileExport(this.onBeforeDownloadFileExport, this);
this.spreadsheetUpload.triggerDownloadSpreadsheet();
},
onBeforeDownloadFileExport: function (event) {
const workbook = event.getParameters().workbook;
event.getParameters().filename = filename + "_modified";
}
Attach async functions to events¶
You can attach async functions to the events by wrapping the function in a Promise. This allows you to send a request to the backend for checks that are not possible in the frontend, for example with a function import.
// Init spreadsheet upload
this.spreadsheetUpload = await this.editFlow
.getView()
.getController()
.getAppComponent()
.createComponent({
usage: 'spreadsheetImporter',
async: true,
componentData: {
context: this,
activateDraft: true
}
});
// Event to check before uploading to app
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachCheckBeforeRead(async function (event) {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
// Example
console.log('Start async wait');
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
console.log('End async wait');
// Don't forget to resolve the promise
resolve();
});
}, this);
Validate the data in the backend with RAP/CAP before creating the entity¶
As explained above, your are able to use async functions to validate the data.
Using this approach, you are able to validate the data in the backend with Actions before creating the entity.
Validating with CAP Backend Actions¶
You can implement backend validation using an unbound action in CAP (Cloud Application Programming model) to check data before it gets saved. You can find the files here:
Here's a complete implementation example:
1. Define the Action in schema.cds¶
// Define action input type
type ShippingDetailCheck {
city : String;
address : String;
row : Integer;
}
// Define action return type
type ShippingDetailResult {
title : String;
row : Integer;
group : Boolean;
rawValue : String;
ui5type: String;
value : String;
}
// Add the action
action checkShippingDetails(shippingDetails : many ShippingDetailCheck) returns {
value : many ShippingDetailResult
};
2. Expose the Action in Your Service (orders-service.cds)¶
service OrdersService {
entity Orders as projection on my.Orders;
entity OrderItems as projection on my.OrderItems;
// ... other entity definitions
// Unbound action to check shipping details against product titles
action checkShippingDetails(shippingDetails : many my.ShippingDetailCheck) returns {
value : many my.ShippingDetailResult
};
}
3. Implement the Action Handler (orders-service.js)¶
const cds = require('@sap/cds');
class OrdersService extends cds.ApplicationService {
/** register custom handlers */
init() {
const { OrderItems } = this.entities;
// Register action handler for checking shipping details
this.on('checkShippingDetails', async req => {
const { shippingDetails } = req.data;
const errors = [];
// Process each shipping detail entry
for (const shippingDetail of shippingDetails) {
const { city, row } = shippingDetail;
if (city) {
try {
// Query order items to see if city name is used in any product title
const orderItems = await SELECT.from(OrderItems).where(`title like '%${city}%'`);
if (orderItems && orderItems.length > 0) {
// Create error for city found in product titles
errors.push({
title: `City "${city}" found in product title`,
row: row || 0,
group: true,
rawValue: city,
messageType: 'Warning',
value: city
});
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error in city check:', error);
errors.push({
title: `Error checking city "${city}"`,
row: row || 0,
group: true,
rawValue: city,
messageType: 'Error',
value: city
});
}
}
}
// Return the list of errors/warnings
return { value: errors };
});
return super.init();
}
}
module.exports = OrdersService;
4. Call the Action from the Frontend (ObjectPageExtController.js)¶
this.spreadsheetUploadTableShipping.attachCheckBeforeRead(async function (event) {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
try {
// Show busy state in the upload dialog
const eventParameters = event.getParameters();
const source = event.getSource();
const uploadDialog = source.spreadsheetUpload.getSpreadsheetUploadDialog();
uploadDialog.setBusyIndicatorDelay(0);
uploadDialog.setBusy(true);
// Get the parsed data from the spreadsheet
const parsedData = eventParameters['parsedData'];
// Prepare shipping details to be checked by the backend
const shippingDetails = [];
for (const [index, row] of parsedData.entries()) {
if (row.city) {
shippingDetails.push({
city: row.city,
address: row.address || '',
row: index + 2 // Adjust for header row and zero-indexing
});
}
}
// Skip check if no shipping details with cities are present
if (shippingDetails.length === 0) {
uploadDialog.setBusy(false);
resolve();
return;
}
// Get the model and call the unbound action
const model = this.getModel();
const actionBinding = model.bindContext('/OrdersService/checkShippingDetails(...)');
actionBinding.setParameter('shippingDetails', shippingDetails);
try {
await actionBinding.execute();
// Get the result from the action
const actionResult = actionBinding.getBoundContext().getObject();
// Add errors to the spreadsheet uploader component to be displayed
if (actionResult && actionResult.value && actionResult.value.length > 0) {
source.addArrayToMessages(actionResult.value);
}
} catch (actionError) {
console.error('Error executing action:', actionError);
source.addArrayToMessages([
{
title: 'Error checking city names',
row: 0,
group: true,
rawValue: 'Error in backend check',
ui5type: 'Error'
}
]);
}
uploadDialog.setBusy(false);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error during city check:', error);
const uploadDialog = event.getSource().spreadsheetUpload.getSpreadsheetUploadDialog();
if (uploadDialog) {
uploadDialog.setBusy(false);
}
}
// Important! Don't forget to resolve the promise
resolve();
});
}, this);
Validating with RAP Backend Actions¶
For SAP S/4HANA or BTP ABAP environments, you can use the RAP (RESTful ABAP Programming) model to implement similar validations using unbound actions.
Warning
This is just sample code to show how it could be done. It is not tested and might not work as expected.
1. Define the Action in Behavior Definition¶
define behavior for ZI_OrderDocument alias Order
{
// ... other behavior definitions
action checkCityNames deep parameter ZI_CITY_CHECK_ROOT
result [0..*] ZI_CITY_CHECK_RETURN;
// ... other behavior definitions
}
2. Implement the Action Handler in Behavior Implementation Class¶
METHOD checkCityNames.
"----------------------------------------------------------------------
" Description: Check city names against product titles
"----------------------------------------------------------------------
DATA: lr_validator TYPE REF TO zcl_city_validator,
lv_isdraft TYPE abp_behv_flag.
DATA(lv_guid) = keys[ 1 ]-Guid.
DATA(shipping_details) = keys[ 1 ]-%param-_shipping.
lr_validator = NEW #( ).
"Take over draft mode
lv_isdraft = keys[ 1 ]-%is_draft.
"Read order data
READ ENTITIES OF ZI_OrderDocument IN LOCAL MODE
ENTITY Order
ALL FIELDS WITH VALUE #( ( Guid = lv_guid
%is_draft = lv_isdraft ) )
RESULT DATA(lt_order).
IF lines( lt_order ) NE 1.
" Return error if order not found
APPEND VALUE #( guid = lv_guid
%param = VALUE zi_city_check_return(
row_number = 0
title = 'Order not found'
messageType = 'E'
value = space ) ) TO result.
RETURN.
ENDIF.
" Loop through all shipping details from Excel
LOOP AT shipping_details ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<detail>).
" Extract city name
DATA(lv_city) = <detail>-city.
IF lv_city IS NOT INITIAL.
" Check if city exists in any product titles
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM zorderitems
WHERE title LIKE '%' && lv_city && '%'
INTO @DATA(lv_count).
IF lv_count > 0.
" Add warning if city is found in product titles
APPEND VALUE #( guid = lv_guid
%param = VALUE zi_city_check_return(
row_number = <detail>-row_number
title = |City "{ lv_city }" found in product title|
messageType = 'W'
value = lv_city ) ) TO result.
ENDIF.
" Additional validations can be added here
" For example, check address format, postal code validity, etc.
lr_validator->check_address_format(
EXPORTING
iv_address = <detail>-address
iv_city = lv_city
iv_row = <detail>-row_number
CHANGING
ct_result = result
).
ENDIF.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
3. Call the Action from Frontend¶
this.spreadsheetUpload.attachCheckBeforeRead(async oEvent => {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
const eventParameter = oEvent.getParameters();
const source = oEvent.getSource();
const uploadDialog = source.spreadsheetUpload.getSpreadsheetUploadDialog();
uploadDialog.setBusyIndicatorDelay(0);
uploadDialog.setBusy(true);
try {
const parsedData = eventParameter['parsedData'];
// Prepare shipping details to be checked by the backend
const shippingDetails = [];
for (const [index, row] of parsedData.entries()) {
if (row.city) {
shippingDetails.push({
city: row.city,
address: row.address || '',
postal_code: row.postalCode || '',
country: row.country || '',
row_number: row.__rowNum__ + 1 // Add 1 to account for header row
});
}
}
// Skip check if no shipping details with cities are present
if (shippingDetails.length === 0) {
uploadDialog.setBusy(false);
resolve();
return;
}
// Prepare action parameter structure
const actionParameterObject = { _shipping: shippingDetails };
// Get context and create action
const context = this.getBindingContext();
const action = this.getModel().bindContext('com.sap.gateway.srvd.orders.v0001.checkCityNames(...)', context);
// Add shipping details as parameters to the action
action.setParameter('_shipping', shippingDetails);
// Execute the action and wait for the result
await action.execute();
// Get results of the backend checks
const actionResult = action.getBoundContext().getObject();
let errorsArray = [];
for (const [index, row] of actionResult.value.entries()) {
const error = {
title: row.title,
row: row.row_number,
group: true,
rawValue: row.value,
ui5type: row.messageType === 'W' ? 'Warning' : row.messageType === 'E' ? 'Error' : 'Information'
};
errorsArray.push(error);
}
if (errorsArray.length > 0) {
// Sort by row number in Excel file
errorsArray.sort((a, b) => a.row - b.row);
// Add errors to the component
source.addArrayToMessages(errorsArray);
}
} catch (error) {
uploadDialog.setBusy(false);
// Add generic error message
source.addArrayToMessages([
{
title: 'Error checking shipping details',
row: 0,
group: true,
rawValue: 'Error in backend validation',
ui5type: 'Error'
}
]);
}
uploadDialog.setBusy(false);
// Important! This must not be deleted
// This tells the component that the code can continue
resolve();
});
}, this);
Both approaches (CAP and RAP) provide powerful ways to validate spreadsheet data on the server side before it's committed to the database, allowing for more complex business rules and validation than what would be possible in the frontend alone.